1. Introduction to BPMN
1.1 What is BPMN?
-
PMN, or Business Process Model and Notation, is a standardized graphical representation for specifying business processes in a workflow. It provides a common language that can be easily understood by all stakeholders, including business analysts, technical developers, and business managers.
Key Features of BPMN
- Visual Representation: BPMN uses standardized symbols and notations to create diagrams that depict the flow of activities within a business process. This visual aspect facilitates communication among stakeholders and enhances understanding of complex processes.
- Levels of Detail: BPMN supports various levels of process modeling, from high-level overviews to detailed representations that can be directly executed in process automation systems. This flexibility allows organizations to tailor their models to specific needs.
- Elements of BPMN: The notation includes several key elements such as:
- Flow Objects: Activities (tasks and subprocesses), Events (start, intermediate, end), and Gateways (decision points).
- Connecting Objects: Sequence flows, message flows, and associations that illustrate how different elements interact.
- Swimlanes: Pools and lanes that categorize responsibilities among different participants in the process.
- Artifacts: Additional information like data objects and annotations that provide context to the process.
Historical Context
BPMN was developed in the early 2000s by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI) to create a unified notation that could bridge the gap between business users and technical execution languages. The first version, BPMN 1.0, was released in 2004 and subsequently adopted as an Object Management Group (OMG) standard.
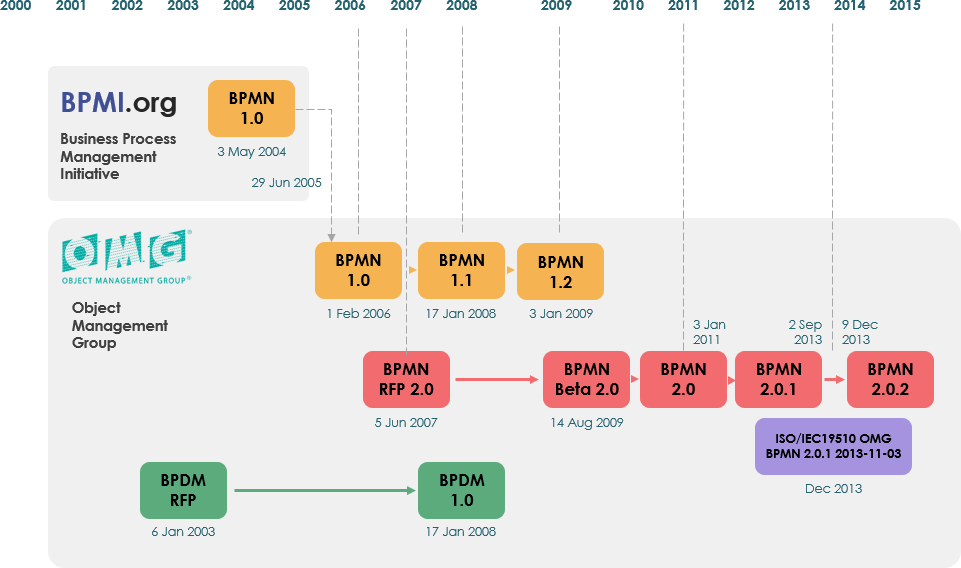
Purpose and Benefits
The primary goal of BPMN is to provide a clear and easy-to-understand method for modeling business processes. This helps organizations improve their process management efforts by ensuring clarity across various departments, facilitating better collaboration, and enabling process automation where applicable. By providing a common language for both business users and IT professionals, BPMN enhances the efficiency of communication and reduces misunderstandings in process design.In summary, BPMN serves as a powerful tool for organizations looking to document, analyze, and improve their business processes through a standardized visual framework.
1.2 Importance of BPMN in Business Process Management
BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) plays a crucial role in Business Process Management (BPM) by providing a standardized method for visualizing and managing business processes. Here are the key reasons highlighting its importance:
1. Standardization of Communication
BPMN offers a common language that bridges the gap between various stakeholders, including business analysts, developers, and managers. This standardization ensures that everyone involved has a clear understanding of the processes being modeled, reducing miscommunication and enhancing collaboration across departments 1.
2. Enhanced Clarity and Understanding
The graphical representation of processes in BPMN makes complex workflows easier to understand. Stakeholders can visualize the flow of activities, decisions, and interactions, which aids in identifying inefficiencies and areas for improvement within the process 2.
3. Facilitation of Process Automation
BPMN not only serves as a modeling tool but also provides a mapping to execution languages like WSBPEL (Web Services Business Process Execution Language). This capability allows organizations to automate business processes effectively, ensuring that the designed processes can be executed by software systems without losing their intended logic 1.
4. Support for Various Process Types
BPMN accommodates different types of processes, including private (internal) and public (external) processes, as well as choreographies that involve interactions between multiple participants. This versatility allows organizations to model a wide range of business scenarios 1.
5. Improved Process Analysis and Monitoring
With BPMN, organizations can analyze their processes more effectively by using standardized metrics and performance indicators. The clarity provided by BPMN diagrams enables better monitoring and management of business processes over time, facilitating continuous improvement efforts 2.
6. Integration with Other Systems
BPMN’s standardized format allows for easier integration with other modeling tools and methodologies. This interoperability is essential for organizations that utilize multiple systems for process management and helps ensure consistency across different platforms 1.
7. Adaptability to Changing Business Needs
As businesses evolve, their processes must adapt accordingly. BPMN provides the flexibility to modify existing process models easily, allowing organizations to respond quickly to new requirements or changes in the market environment 2.In summary, BPMN is vital in business process management as it enhances communication, clarity, automation capabilities, analytical insights, integration potential, and adaptability—factors that are crucial for achieving operational efficiency and effectiveness in modern organizations.
1.3 Overview of BPMN 2.0
1. Enhanced Notation
BPMN 2.0 introduces a more comprehensive set of symbols and notations that improve the clarity and expressiveness of business process diagrams. This includes new types of events, such as non-interrupting events, which allow for more complex process flows without halting ongoing activities.
2. Support for Choreography and Collaboration
The new version emphasizes the importance of choreography (the interaction between multiple participants) alongside orchestration (the internal workings of a single organization). BPMN 2.0 allows for explicit choreography diagrams, making it easier to model interactions between different business entities without deriving them from message exchanges alone.
3. Improved Process Interchange
BPMN 2.0 provides an interchange format that enables the portability of process definitions across different modeling tools. This means that users can create BPMN diagrams in one tool and seamlessly transfer them to another, facilitating collaboration and reducing compatibility issues.
4. Advanced Modeling Capabilities
The standard incorporates advanced modeling concepts such as exception handling, transactions, and compensation. These features allow for more sophisticated representations of business processes, accommodating real-world complexities like error management and process recovery.
5. Formalization of Execution Semantics
BPMN 2.0 formalizes execution semantics, which clarifies how BPMN diagrams should be interpreted by software systems. This ensures that models can be executed consistently across different platforms, enhancing automation capabilities.
6. Multi-Instance Activities
BPMN 2.0 introduces the concept of multi-instance activities, allowing for tasks to be executed multiple times in parallel or sequentially based on defined conditions. This feature is useful for processes that require repetitive actions or batch processing.
7. Artifacts and Data Objects
The updated standard includes artifacts like data objects, groups, and annotations that provide additional context to the process models without cluttering the main flow diagram. This helps in capturing relevant information about data inputs and outputs associated with various activities.
Conclusion
BPMN 2.0 represents a significant advancement in business process modeling by enhancing notation clarity, supporting collaborative processes, improving interchangeability between tools, and formalizing execution semantics. These improvements make BPMN a powerful tool for organizations seeking to effectively document, analyze, and automate their business processes while ensuring clear communication among all stakeholders involved.
References
- Understanding BPMN: A Comprehensive Overview – Visual Paradigm
- Streamlining Business Processes with Visual Paradigm’s BPMN – Archimetric
- Business Process Design with Powerful BPMN Software – Visual Paradigm
- Camunda vs Visual Paradigm Comparison – PeerSpot
- Review: First Impressions of Visual Paradigm Professional – Visual Paradigm Forums
- Online BPMN Diagram Tool – Visual Paradigm Online
- Business Process Modeling Tool – Visual Paradigm