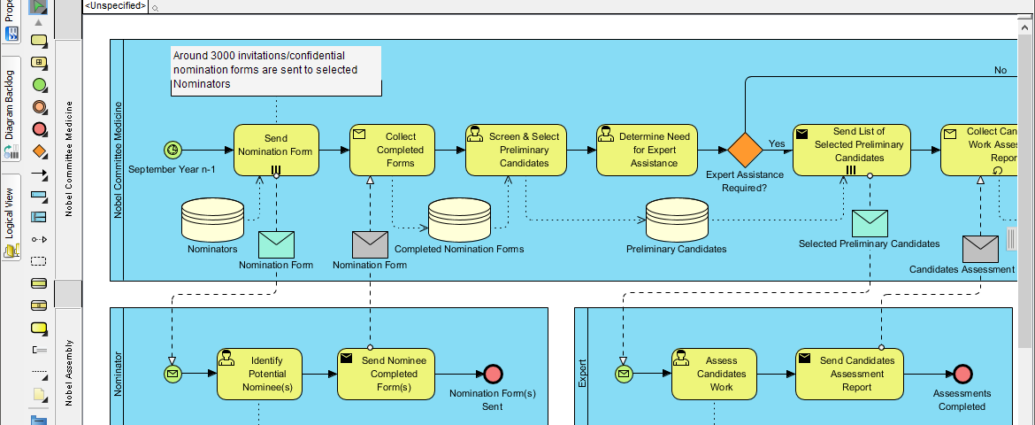
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a standardized graphical representation for specifying business processes in a workflow. Developed by the Object Management Group (OMG), BPMN provides a visual language that is easily understandable by all stakeholders, including business analysts, technical developers, and business managers. This tutorial will guide you through the essential elements of BPMN and how to create your own BPMN diagrams.
Key BPMN Elements
BPMN uses a variety of symbols to represent different aspects of business processes. The main categories of BPMN elements include:
Flow Objects
- Events: Represent something that happens during the process (e.g., start or end).
- Activities: Tasks or work performed in the process.
- Gateways: Decision points that control the flow based on certain conditions.
Connecting Objects
- Sequence Flows: Solid lines with arrows indicating the order of activities.
- Message Flows: Dashed lines showing communication between different participants.
Swimlanes
- Pools: Represent major participants in a process, such as departments or organizations.
- Lanes: Subdivisions within pools that specify responsibilities for particular tasks.
Creating a BPMN Diagram
To create a BPMN diagram, follow these steps:
1. Define Your Process
Start by clearly defining the business process you want to model. Identify the start and end points, as well as key activities and decisions involved.
2. Choose a BPMN Tool
Select a tool for creating your BPMN diagram. Popular options include:
- Lucidchart
- Camunda Modeler
- ProcessMaker
3. Add Flow Objects
Begin by placing flow objects on your diagram:
- Start Event: Mark the beginning of your process.
- Activities: Add tasks that need to be performed.
- Gateways: Insert decision points where necessary.
4. Connect the Objects
Use sequence flows to connect your flow objects in the order they occur. Ensure that message flows are used when depicting communication between different pools.
5. Organize with Swimlanes
Utilize pools and lanes to clarify roles and responsibilities within your process. Name each pool and lane appropriately to reflect their functions.
6. Review and Refine
Once your diagram is complete, review it for clarity and accuracy. Ensure all stakeholders can understand the process flow without confusion.
Best Practices for BPMN Modeling
- Keep It Simple: Aim for clarity over complexity; avoid overcrowding your diagram with too many elements.
- Use Standard Notations: Adhere to BPMN standards to ensure consistency and understanding across different users.
- Label Clearly: Use descriptive labels for activities and events to enhance comprehension.
- Iterate Based on Feedback: Share your diagram with stakeholders for feedback and make necessary adjustments.
Unlock the Power of BPMN Modeling with Visual Paradigm
In today’s fast-paced business environment, understanding and optimizing your business processes is crucial for success. Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) provides a graphical representation of business workflows that anyone, from business analysts to stakeholders, can easily understand. Visual Paradigm stands out as a leading BPMN modeling software, offering an intuitive and powerful toolset to create professional Business Process Diagrams (BPDs) quickly and smoothly.

Why Choose Visual Paradigm for BPMN Modeling?
1. Intuitive BPMN 2.0 Modeler Visual Paradigm features an intuitive BPMN 2.0 modeler that allows you to create professional Business Process Diagrams with ease. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to BPMN, our user-friendly interface ensures a seamless experience.
2. Process Drill-Down Dive deep into your business processes with our Process Drill-Down feature. You can “open up” a sub-process and model the lower level of process flow in another business process diagram. Easily collapse sub-processes to hide details or expand them to view lower-level process flows, providing a comprehensive view of your workflows.

3. Integration with Multiple Standards Visual Paradigm is an all-rounded visual modeling tool that supports a wide range of diagrams and integrates them to maximize the effectiveness of visual modeling. In a process design, you can map the process flow with other modeling artifacts such as UML shapes, ERD entities, wireframes, and more. This flexibility ensures that you can tailor your models to fit your specific needs.

4. Working Procedure Editor While a BPD provides a bird’s eye view of a business process, the operational procedures of individual business activities can be further specified in the Working Procedure Editor. This feature allows you to output a process specification that contains both the process diagram and the working procedure, making it easy to share guidelines with your team.
5. As-is and To-be Process Modeling Visual Paradigm enables you to produce a target process model (To-be) from the baseline (As-is) and start editing the target to represent the expected result of process improvement or re-engineering. Traceability is maintained in the background, allowing you to navigate through the two models smoothly.

6. RACI and CRUD Charts RACI charts are matrices that present the different responsibilities of diverse people, teams, departments, or any other business units in completing business activities. Visual Paradigm allows you to create RACI charts with rows of participants and columns of business activities, marking cells with letters R, A, C, or I to represent specific responsibilities. Additionally, you can create CRUD charts or any custom chart to suit your needs.

7. Process Animation Bring your business process designs to life with our Process Animation tool. This feature clears the barrier encountered in studying process flows with static images by analyzing process flows and converting them into animations. These animations can be viewed in motion by you, your clients, and colleagues, providing a dynamic way to understand workflows.
8. Process Simulation Visually simulate the execution of business processes to study resource consumption, evaluate costs, identify bottlenecks, and trial run possible process improvement options. With features like resource allocation, configurable time scales, cost evaluation, completion charts, resource usage charts, and queue time charts, you can gain deep insights into your processes.
Conclusion
BPMN is a powerful tool for visualizing business processes, facilitating communication among stakeholders, and improving operational efficiency. By following this tutorial, you can create effective BPMN diagrams that accurately represent your business processes, aiding in analysis and improvement efforts.
Visual Paradigm is more than just a BPMN modeling tool; it’s a comprehensive solution that empowers you to analyze, improve, and optimize your business processes. With its intuitive interface, powerful features, and flexibility, Visual Paradigm is the go-to choice for businesses looking to enhance their process management capabilities.
Don’t let complex business processes hold you back. Try Visual Paradigm today and experience the difference for yourself!
References
- BPMN Modeling and Reference Guide: This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at BPMN elements, including gateways, events, and tasks. It discusses modeling issues, the importance of process modeling, and offers scenario-based examples to illustrate BPMN functionality. The guide serves as a foundational resource for both beginners and experienced users looking to deepen their understanding of BPMN concepts and applications. BPMN Modeling and Reference Guide
- Visual Paradigm Official Documentation: Visual Paradigm offers extensive documentation that covers everything from basic BPMN concepts to advanced modeling techniques. This resource is invaluable for users seeking to learn how to effectively use the tool for their specific BPMN modeling needs. Visual Paradigm Official Documentation
- Online Tutorials and Webinars: Visual Paradigm frequently hosts webinars and provides online tutorials that cover various aspects of BPMN modeling. These resources are designed to help users become proficient in using the software while understanding BPMN standards. Online Tutorials and Webinars
- BPMN Activity Types Explained: This guide explains the different types of activities in BPMN, providing a clear understanding of how to use them in process modeling. BPMN Activity Types Explained
- BPMN Orchestration vs Choreography vs Collaboration: This resource compares different BPMN diagram types, explaining the differences between orchestration, choreography, and collaboration in BPMN. BPMN Orchestration vs Choreography vs Collaboration