Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a standardized graphical notation for depicting business processes in a workflow. One of the key components of BPMN is swimlanes, which are used to organize and clarify the roles and responsibilities within a process. This guide will explore what swimlanes are, their types, and when to use them effectively.
What are Swimlanes?
Swimlanes are visual elements in BPMN diagrams that help partition activities into distinct categories, typically representing different participants or roles involved in a process. They enhance clarity by delineating who is responsible for which tasks, making it easier to understand complex workflows.
Types of Swimlanes
- Pools:
- Pools represent major participants in a process, such as organizations or departments. Each pool acts as a container for one participant’s activities in a collaborative business process diagram.
- A pool can represent either a general business role (e.g., buyer, supplier) or a specific entity (e.g., FedEx as the shipper) 1.
- Lanes:
- Lanes are sub-partitions within pools that categorize activities based on specific roles or functions. For example, lanes can represent different departments (e.g., Sales, Marketing) or functional areas (e.g., Customer Service).
- Lanes can be nested to create hierarchical structures, allowing for more detailed organization of responsibilities 12.
Why Use Swimlanes?
Swimlanes serve several important purposes in process modeling:
- Clarity: By visually separating responsibilities, swimlanes help stakeholders quickly identify who is accountable for each part of the process.
- Collaboration: In collaborative processes involving multiple participants, swimlanes illustrate how different entities interact and communicate through message flows.
- Organization: They enable modelers to group related activities logically, making it easier to analyze and optimize processes.
- Complexity Management: For complex processes with many actors, swimlanes simplify understanding by breaking down interactions into manageable sections.
When to Use Swimlanes
Swimlanes are particularly useful in the following scenarios:
- Collaborative Processes: When multiple participants or departments are involved in a process, using pools and lanes clarifies interactions and responsibilities.
- Role-Based Analysis: When analyzing workflows based on specific roles or functions within an organization, lanes help highlight differences in responsibilities.
- Process Improvement Initiatives: In efforts to streamline operations or improve efficiency, swimlanes can reveal bottlenecks or overlaps in responsibilities that may need addressing.
- Training and Documentation: Swimlanes provide clear visual aids for training new employees or documenting processes for compliance purposes.
Swimlane BPMN Example
Explanation of BPMN and Swimlanes
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a standardized graphical representation used to model business processes. It provides a visual way to understand the flow of activities, the participants involved, and the decisions made within a process.
Swimlanes in BPMN are used to organize and categorize activities within a process. They help in visually separating different roles, departments, or systems involved in the process. Swimlanes can be horizontal or vertical and are typically labeled to indicate the responsible entity for the activities within that lane.
Interpretation of the Attached BPMN Diagram
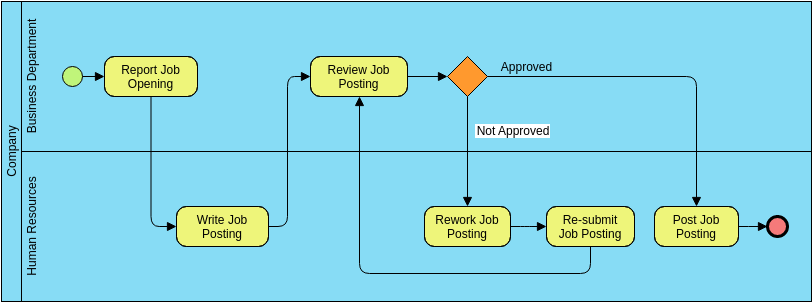
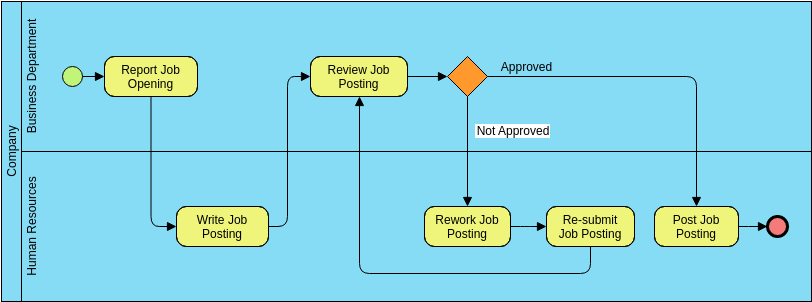
The BPMN diagram illustrates the process of job posting within a company. The diagram is divided into two swimlanes: “Business Department” and “Human Resources (HR).”
Swimlanes and Activities
- Business Department Swimlane:
- Report Job Opening: The process starts with the Business Department reporting a job opening. This is the initial task that triggers the job posting process.
- Human Resources (HR) Swimlane:
- Write Job Posting: HR writes the job posting based on the information provided by the Business Department.
- Review Job Posting: The job posting is then reviewed. This could be an internal review within HR or a review by the Business Department.
- Decision Gateway (Approved/Not Approved): After the review, a decision is made whether the job posting is approved or not approved. This is represented by a diamond-shaped gateway.
- If Approved: If the job posting is approved, it moves directly to the “Post Job Posting” task.
- If Not Approved: If the job posting is not approved, it goes through a rework process:
- Rework Job Posting: HR reworks the job posting based on the feedback received.
- Re-submit Job Posting: The reworked job posting is resubmitted for review.
- The process then loops back to the “Review Job Posting” task.
- Post Job Posting: Once the job posting is approved, it is posted. This is the final task in the process, represented by an end event (red circle).
Flow of the Process
- The Business Department initiates the process by reporting a job opening.
- HR writes the job posting.
- The job posting is reviewed.
- A decision is made based on the review:
- If approved, the job posting is posted.
- If not approved, the job posting is reworked and resubmitted for review.
- The process continues until the job posting is approved and posted.
The BPMN diagram provides a clear visualization of the job posting process, showing the interaction between the Business Department and HR. It highlights the decision points and the flow of activities, making it easier to understand and manage the process. The use of swimlanes helps in identifying the responsibilities of each department involved in the job posting process.
Conclusion
Incorporating swimlanes into BPMN diagrams is essential for effective process modeling. They not only enhance clarity and organization but also facilitate better communication among stakeholders. Understanding when and how to use pools and lanes will significantly improve the quality of your business process documentation and analysis. Whether you are modeling simple workflows or complex interactions between multiple entities, swimlanes are a powerful tool in your BPMN toolkit.
References
- What is BPMN?
- BPMN Tutorial with Example – The Leave Application Process
- BPMN Modeling and Reference Guide: This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at BPMN elements, including gateways, events, and tasks. It discusses modeling issues, the importance of process modeling, and offers scenario-based examples to illustrate BPMN functionality. The guide serves as a foundational resource for both beginners and experienced users looking to deepen their understanding of BPMN concepts and applications. BPMN Modeling and Reference Guide
- Visual Paradigm Official Documentation: Visual Paradigm offers extensive documentation that covers everything from basic BPMN concepts to advanced modeling techniques. This resource is invaluable for users seeking to learn how to effectively use the tool for their specific BPMN modeling needs. Visual Paradigm Official Documentation
- Online Tutorials and Webinars: Visual Paradigm frequently hosts webinars and provides online tutorials that cover various aspects of BPMN modeling. These resources are designed to help users become proficient in using the software while understanding BPMN standards. Online Tutorials and Webinars
- BPMN Activity Types Explained: This guide explains the different types of activities in BPMN, providing a clear understanding of how to use them in process modeling. BPMN Activity Types Explained
- BPMN Orchestration vs Choreography vs Collaboration: This resource compares different BPMN diagram types, explaining the differences between orchestration, choreography, and collaboration in BPMN. BPMN Orchestration vs Choreography vs Collaboration